Discover the Annual Information Statement (AIS) under Income Tax to understand its features, benefits, and differences from Form 26AS. Learn how to access and review your AIS for hassle-free tax compliance and enhanced transparency.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Indian Income Tax Department has implemented the AIS compliance system to increase transparency. Through the AIS, taxpayers can view a complete list of financial transactions that different reportable entities share with the Income Tax Department. The article examines the AIS system by explaining its detailed importance and differences compared to Form 26AS while providing steps for taxpayers to validate their AIS data accuracy.
What is the Annual Information Statement (AIS)?
The AIS is an informative statement provided by the Income Tax Department. It collects information from various entities like banks, stock brokers, financial institutions, registrars, etc. Such institutions are called Reportable Entities. They must submit information related to particular transactions upon meeting specific rule sets defined by the Income Tax Department. For example, your stock broker must provide details of your stock market transactions, including dividends you received, which are captured in the Annual Information Statement.
An Annual Information Statement aims to reduce errors and bring transparency while filing Income Tax Returns. Upon reviewing such an AIS, a taxpayer becomes aware of what information related to him is available with the department, which reduces the chances of underreporting income.
Key Features of the Annual Information Statement (AIS)
1. Comprehensive Information
The AIS provides a detailed summary of a taxpayer’s financial transactions, including:
- Salary Income: Details of salary income as reported by the employer.
- Interest Income: Interest earned on savings accounts, fixed deposits, and other interest-bearing instruments.
- Dividend Income: Dividends received from shares and mutual funds.
- Mutual Fund Transactions: Details of purchases and sales of mutual fund units.
- Foreign Remittances: Information on foreign remittances made.
- Rent Received: Details of rent received from the property.
- Purchase and Sale of Securities: Transactions involving purchasing and selling stocks, bonds, and other securities.
- Credit Card Payments: Details of credit card payments made during the year.
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): Information on TDS deducted by various entities.
- Property Transactions: Purchase and sale of immovable property.
A Reportable Entity reports this information upon exceeding a specific transaction threshold limit. That means you have made the abovementioned transactions, which are not reflected in AIS. The reason is that they might be below the specified reporting threshold, or the reporting entity has failed to report the same. Also, the above list is illustrative and not exhaustive.
2. Feedback Mechanism
The taxpayers can provide feedback on information in AIS if they spot any inaccuracy, which helps ensure the mechanism’s accuracy.
3. Integration with Form 26AS
The AIS also captures information from your Form 26AS. Form 26AS provides your TDS and TCS data; this includes data such as from whom you have received the sum, the nature of the sum, the amount, etc. AIS extracts such information from Form 26AS to generate the statement.
How do you access the annual information statement (AIS)?
Accessing the AIS is a straightforward process. Here are the steps to view and download your AIS:
Step 1: Go to the official Income Tax portal by clicking on https://www.incometax.gov.in/. The screen will appear as follows:

Step 2: Click on the “Login” option at the top right, as shown in the above image. A new screen will then appear as follows. Enter your PAN (Permanent Account Number) as “User ID” and then click on continue.
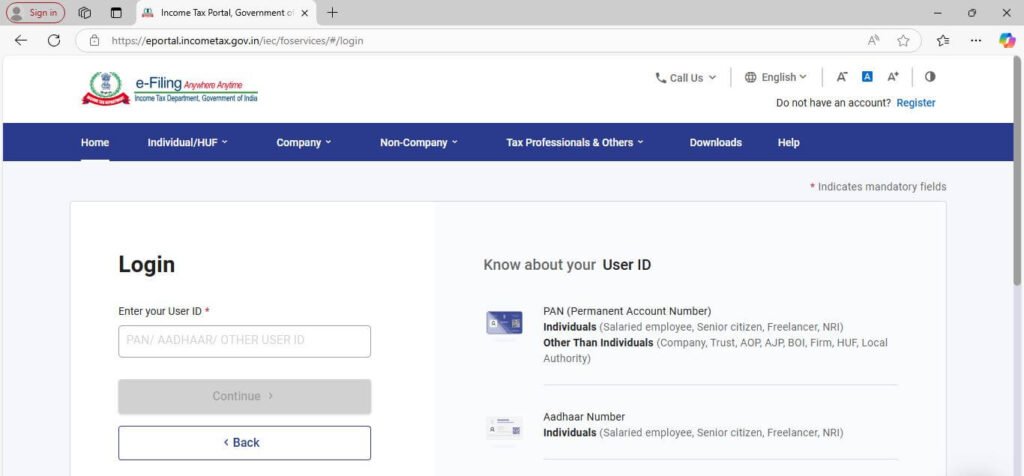
Step 3: Upon clicking “Continue,” a new screen will appear asking for your password; enter the same and “tick” the dialogue box confirming your secret message as shown below:

Step 4: You are now logged into your Income Tax Portal. Now click on “AIS,” as shown in the image below:
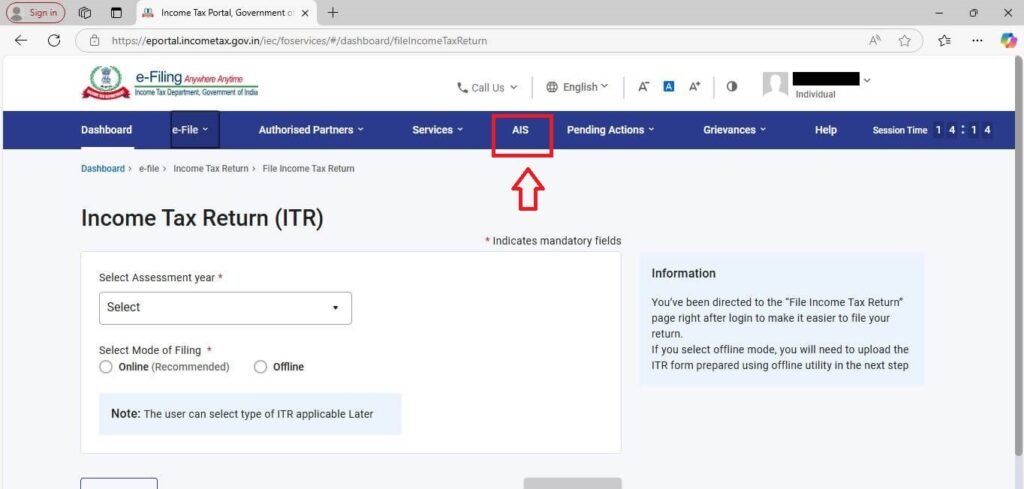
Step 5: You will be asked for redirection confirmation. Click on “Proceed”.
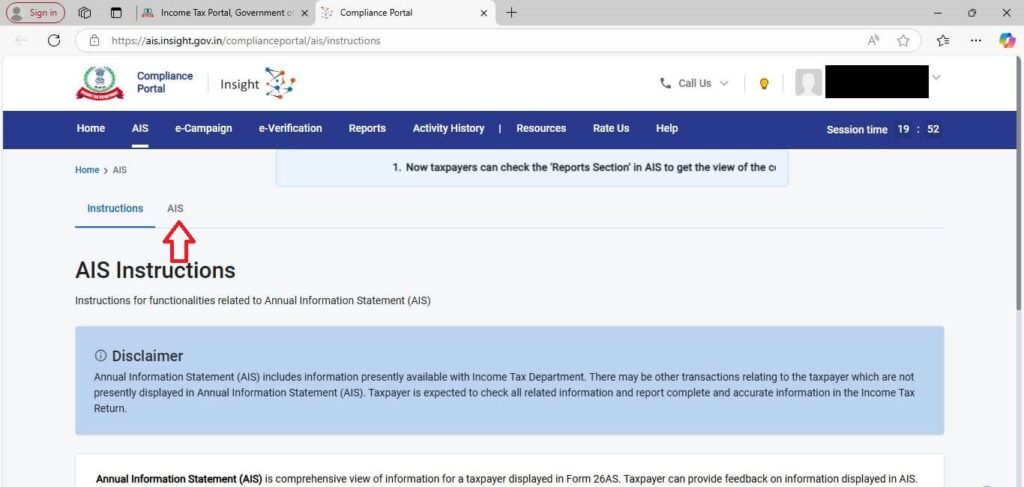
Step 6: Now, a new webpage will open as follows. Click on “AIS” as shown in the following image.
Step 7: On the next page, you can see two options: “Taxpayer Information Summary (TIS)” and “Annual Information Statement (AIS).” A TIS will provide you with a summary of your data, whereas an AIS will provide detailed information.
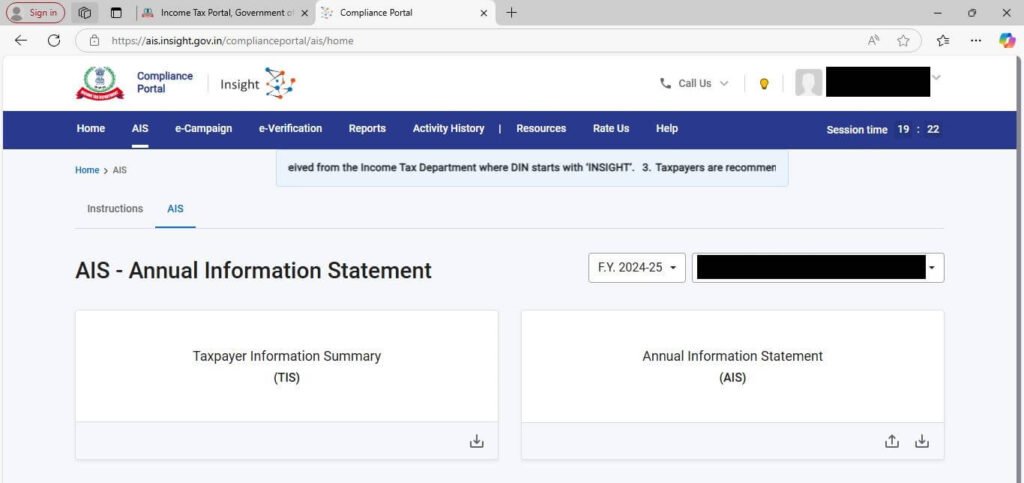
Step 8: Upon clicking TIS, you will see the following page with available information.
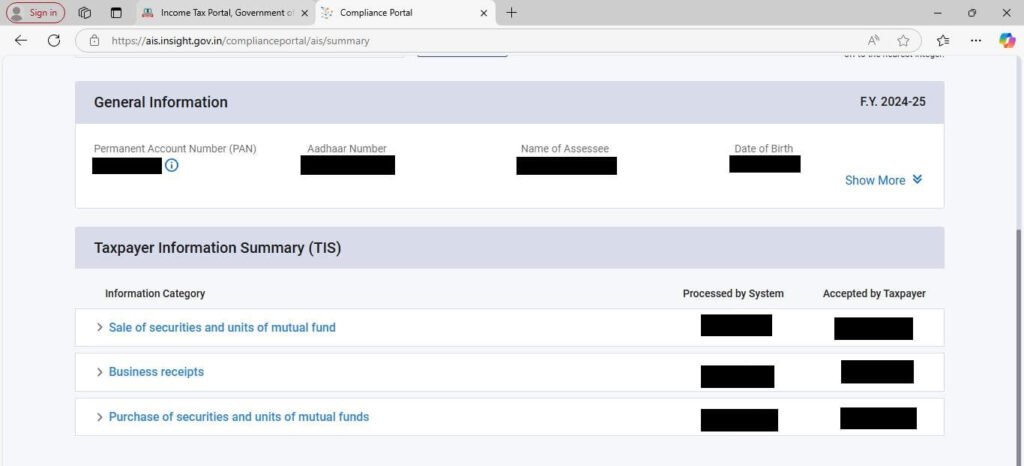
Further, you can go to the AIS by scrolling up and selecting Annual Information Statement. Now, you will get the following webpage.

Step 9: Further, if you want to download the Annual Information Statement, scroll up and click on “Download” as shown below:
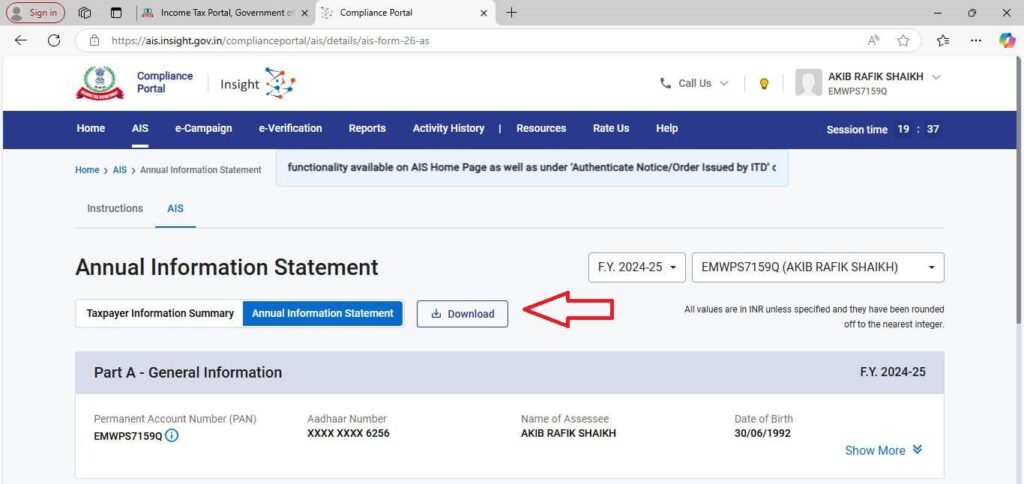
Step 10: A page will open upon clicking “Download. ” Click the “Download” option opposite the “Annual Information Statement (AIS)—PDF.”

Upon opening the downloaded PDF, you will be asked for a password. The password to open the AIS will be a combination of your Permanent Account Number(PAN), in small case, and your Date of birth. If your PAN is ABCDE1234F and your date of birth is 01/01/2001, then your password will be abcde1234f01012001
Importance of the AIS for Taxpayers
The AIS is a valuable tool for taxpayers for several reasons:
1. Enhanced Transparency
The AIS provides taxpayers with a critical view of their financial transactions, which helps reduce the possibility of errors in tax filings. By reviewing detailed information on their income and expenses, taxpayers can take appropriate actions and precautions while preparing their returns.
2. Reduced Risk of Scrutiny
By ensuring that the information in the AIS is reflected in their tax filings, taxpayers can reduce the risk of scrutiny from the tax authorities. Discrepancies in tax returns are a common trigger for notices, and the AIS helps minimize such discrepancies.
3. Empowerment Through Feedback
The feedback mechanism in the AIS empowers taxpayers to take control of their financial data. If taxpayers identify any inaccuracies, they can provide feedback to the Income Tax Department, ensuring their financial information is correct and up-to-date.
Conclusion
The Annual Information Statement (AIS) is a significant document from the taxpayer’s point of view. AIS empowers taxpayers to file accurate and complete tax returns, reducing the risk of scrutiny and disputes with the tax authorities.
As a taxpayer, it is essential to regularly review your AIS, reconcile it with your financial records, and provide timely feedback on any discrepancies.
Embrace the AIS and take the first step towards a more transparent and efficient tax filing process.
Love reading our articles; please have a look on our article for STCG on Shares.
(All due care has been taken to ensure accuracy and reliability in preparing this article. However, tax laws and financial regulations are subject to change, and individual circumstances may vary. Therefore, we strongly recommend consulting a qualified Chartered Accountant (CA) or tax consultant before making any financial decisions or acting based on the information provided. We shall not be held responsible for any damages, losses, or penalties incurred due to reliance on this article.)